|
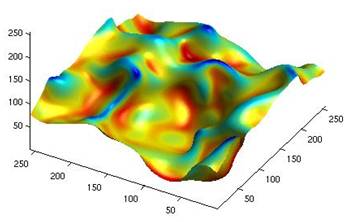
DNS results of a premixed flame surface wrinkled by turbulence and its own (downwards) propagation. The flame surface is coloured by the surface curvature. |
|
Dr. Stephen Tullis
|

|
Home |
|
People |
|
Research |
|
Publications |
|
Courses |
|
Contact |
|
Particle flows and dispersion in turbulence
The dispersion of dilute particulates is studied using direct numerical simulation. The dispersion is affected by the size and density of the particles relative to the turbulence, with preferential concentration occurring when the Stokes number is ~1. A secondary objective is the development of RANS models based on improved incorporation of the physics from the DNS results. This particle work is done in collaboration with Dr. M. Lightstone.
Direct numerical simulation of premixed combustion
Direct Numerical Simulations (DNS) are used to help understand some of the underlying physics involved in the interaction between turbulence and flame dynamics in premixed combustion. The results of these large and computationally expensive simulations can also be used in the development of improved subgrid scale models for Large Eddy Simulations (LES) of turbulent reacting flows. LES of the flows in gas turbine combustors (and other flows of engineering interest, where turbulence plays a crucial role in performance) is one of the ultimate outcomes of this work. The computational resources of Sharcnet are used in this work.
|